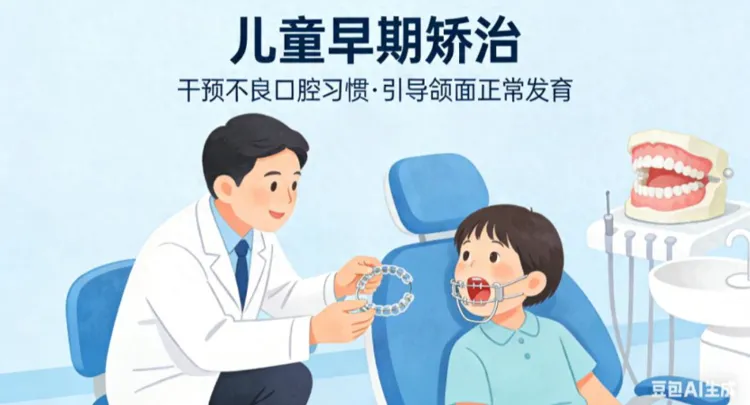
Top dental issues in children that can impact appearance and health
Author: Li Yufeng, Director and Chief Physician of the Department of Stomatology at Changsha Fourth Hospital. Reviewer: Luo Qian, Special Contributor from Hunan Medical Chat. Production/Organizational Information: Department of Stomatology at Changsha Fourth Hospital. Introduction: Experts emphasize that early oral health in children is crucial for long-term appearance and function; prompt consultations are highly recommended.
Issues such as reverse bite, small chin, chronic oral breathing, and thumb sucking are prevalent in children's growth and development yet are often overlooked by parents. Missing the critical intervention periods for jawbone growth can negatively impact facial shape and oral function and may accompany speech abnormalities and social challenges. Li Yufeng, the Director and Chief Physician of the Department of Stomatology at the Fourth Hospital of Changsha, emphasizes the importance of recognizing the golden window for children's jawbone growth and conducting scientifically informed early interventions to ensure their oral health and facial development.
Understanding Early Intervention: Before delving into early orthodontic treatment, it is essential to grasp what malocclusion is — it signifies dental, jawbone, and craniofacial deformities in children caused by genetic and environmental factors during growth.
Early orthodontic treatment encompasses preventive, interceptive, corrective, and guiding therapies for dental and jaw deformities, particularly during early growth stages—typically around the peak periods of puberty. The objective is to create and maintain a healthy environment for the appropriate development of the oral and jaw systems, thereby facilitating the children's facial and psychological well-being and instilling confidence in their smiles.
Maximizing Results Through Staged Intervention: Early treatment effectiveness doesn’t depend solely on initiating it sooner, but rather on addressing the correct issues at the right times. We classify the critical treatment periods into three distinct stages.
1. Primary teeth stage (3-5 years): Focuses on eliminating detrimental habits like thumb sucking, tongue thrusting, mouth breathing, and abnormal swallowing.
2. Mixed dentition period (ages 6-12): Considered the golden window for early orthodontic treatment. At this stage, children possess significant jawbone growth potential. Proper orthodontic appliances can be employed to facilitate intervention for existing or potential malocclusions, guiding jawbone development accordingly.
3. Early permanent teeth stage (around 12-15 years): This phase includes comprehensive orthodontic treatment, allowing the resolution of ongoing challenges from previous interventions or more complex deformities that may not have been timely identified.
Identifying Early Intervention Needs: If you recognize any of the following signs in your child, consult a dental department promptly:
1. Reverse bite (underbite): When the lower teeth overlap the upper teeth, it indicates a need for early intervention.
2. Receding chin: Notably small and posteriorly positioned chin, resembling a bird's beak from the profile.
3. Anterior open bite: Upper and lower front teeth don't touch, often associated with long-term harmful habits like tongue thrusting.
4. Severe deep overbite: Upper front teeth excessively overlap lower front teeth, potentially harming the upper gum tissue.
5. Narrow dental arch: Insufficient width causing issues like posterior crossbite or dental crowding.
6. Long-term mouth breathing: Can lead to an open-lipped appearance, exposed gums, and elongated facial structure.
7. Abnormal swallowing or tongue-thrust habits: Frequent tongue pressure between the teeth may impede normal tooth eruption and jawbone development.
8. Persistent habits like thumb sucking or lip biting (especially the lower lip): Can adversely affect tooth alignment and jawbone development.
During the correction period, parental responsibilities include:
1. Monitoring children for proper oral hygiene.
2. Guiding children in overcoming negative habits such as finger biting and mouth breathing.
3. Scheduling regular follow-ups aligned with growth trajectories.
4. Providing psychological support: Children may feel inferior while wearing braces; parents should encourage them by emphasizing that this process enhances their smiles, promoting confidence and active cooperation with treatment.
Li Yufeng stresses that early detection, diagnosis, and intervention are key to helping children avoid unnecessary orthodontic challenges while safeguarding their jaw and facial health and preserving confident smiles. The Department of Stomatology at Changsha Fourth Hospital is dedicated to using expert techniques and considerate service to protect the bright smiles of children.
Special contributor: Luo Qian, Changsha Fourth Hospital.
Follow @HunanMedicalChat for more health science information!
Editing: ZS.
© 2025 Health Tribe.